Pregnancy is a special time for women, and should not be taken for granted. Proper nutrition is crucial for the health of you and your child. In fact, studies show that what you eat and drink, how physically active you are, and how much you weigh all have an effect on the baby’s present and future growth. Therefore, food must be chosen wisely – not just to suit the palate, but to nurture the baby as well.
There are two factors that must be considered when it comes to pregnancy nutrition – what to eat and how much weight to gain. Many women think that pregnancy is a great excuse to gain weight. However, you shouldn’t go overboard. You do not need to consume more calories than your normally do during the first trimester. Only after the 12th week you can add 300 calories more to your normal daily intake.
Here are some special considerations on pregnancy nutrition:
- Do not eat undercooked meats or seafood.
Eating undercooked meats and seafood can cause diseases such as toxoplasmosis and salmonellosis. These can potentially cause stillbirth, fetal defects, infection, or health problems after birth.
- Reduce your risk for listeriosis.
Listeriosis is a disease caused by bacteria found in soft cheese, raw vegetables, and unpasteurized milk. Wash fruits and vegetables before eating, stick with hard cheeses, like parmesan and cheddar, and make sure your milk is pasteurized.
- Limit your caffeine intake.
You should limit your daily intake of caffeine to 200 mg (12 oz cup). Studies show that women who consumer over 200 mg of caffeine per day have a higher risk for miscarriage, stillbirth, and preterm birth. You may also want to cut back on tea, coffee, soft drinks, chocolate, and energy drinks, as they contain phenols that prevent iron absorption.
- Consume plenty of omega-3 fatty acids.
Studies show that omega-3 has positive effects on the baby’s eyes and brain. You can take at least 400 mg of mercury-free DHA supplements, or be sure you’re eating foods rich in these fatty acids. The best sources are cold water fish such as sardines, tuna, herring, salmon, and anchovies.
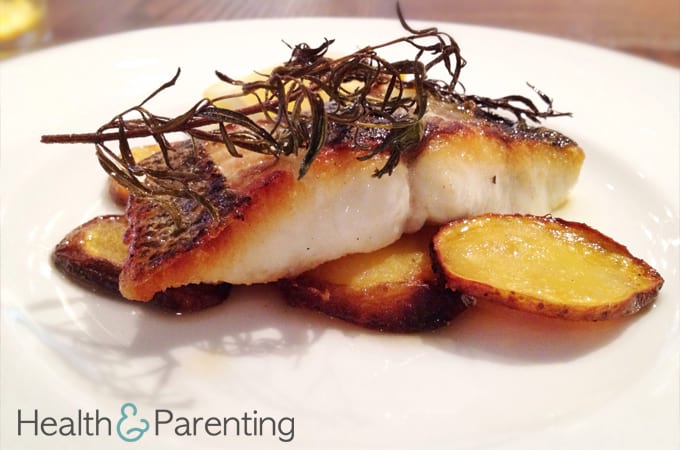
- Stay away from eating certain fish: mackerel, shark, tile fish, tuna steaks, albacore tuna, and swordfish.
These fishes contain high levels of mercury which may have neurological effects on your baby. Limit fish intake to no more than 12 ounces per week, and stick with fish like salmon.
- Avoid any alcoholic beverages.
Heavy alcohol drinking can cause birth defects. It can also cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) which is characterized by speech and language delays, small head size, abnormal facial features, learning disability, and many other problems.
- Take your prenatal vitamins regularly.
Prenatal vitamins are essential for pregnant women as they provide more folic acid and iron, necessary all throughout the pregnancy for the development of the baby’s brain and spinal cord.
Written by Team Health & Parenting
This information is not intended to replace the advice of a trained medical doctor. Health & Parenting Ltd disclaims any liability for the decisions you make based on this information, which is provided to you on a general information basis only and not as a substitute for personalized medical advice. All contents copyright © Health & Parenting Ltd 2018. All rights reserved.